Financial spread betting is betting on whether the price of a financial product (index, stock, bond, or commodity) will rise or fall without actually owning the product. It effectively indicates that you’re wagering solely on the market’s price. As a result, you’re agreeing with the Spread betting provider that if you lose money on a bet, money from your account will be sent to them, and vice versa if you win money on a bet, money from their account will be transferred to your account. The bets in this sort of spread betting are placed in GBP per point/tick.
Financial spread betting is a popular way to speculate on price movements in global financial markets without owning the underlying asset. It allows traders to take positions on the direction of markets like forex, indices, commodities, stocks, ETFs, and more — using leverage. Spread betting itself isn’t investing in the asset; it’s making a bet on price movement. If you’re right, you profit based on how much the market moves in your favor. If you’re wrong, you lose.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down how financial spread betting works in 2026, how costs and profits are calculated, key regulations, strategies, risks, tax implications (especially relevant in the UK and other jurisdictions where it’s recognized), and how traders can approach it responsibly.
Spread betting can be capital-gains tax free in some cases, but it’s better to consult with a tax specialist regarding this. For more information on the potential benefits of trading via spread betting rather than cfds you can check this article.
Broker Review Contents
How Financial Spread Betting Works
At its core, spread betting involves placing a bet on a market’s future price direction:
- A “buy” (long) bet if you think the price will rise
- A “sell” (short) bet if you think the price will fall
When you place a spread bet, you see two prices quoted by your broker:
- Bid (sell) price
- Ask (buy) price
The difference between these two (the spread) is the broker’s charge and your cost of entry.
Practical Example
Let’s say the FTSE 100 is quoted as:
- Buy: 7,100
- Sell: 7,080
Spread: 20 points
If you bet £10 per point up at 7,100 and close it at 7,140 (a 40-point move), your profit would be:
40 points × £10 = £400 (minus costs).
Conversely, if the market moved against you by 40 points:
40 points × £10 = £400 loss.
This example shows how spread betting profits and losses are directly tied to points moved × stake per point.
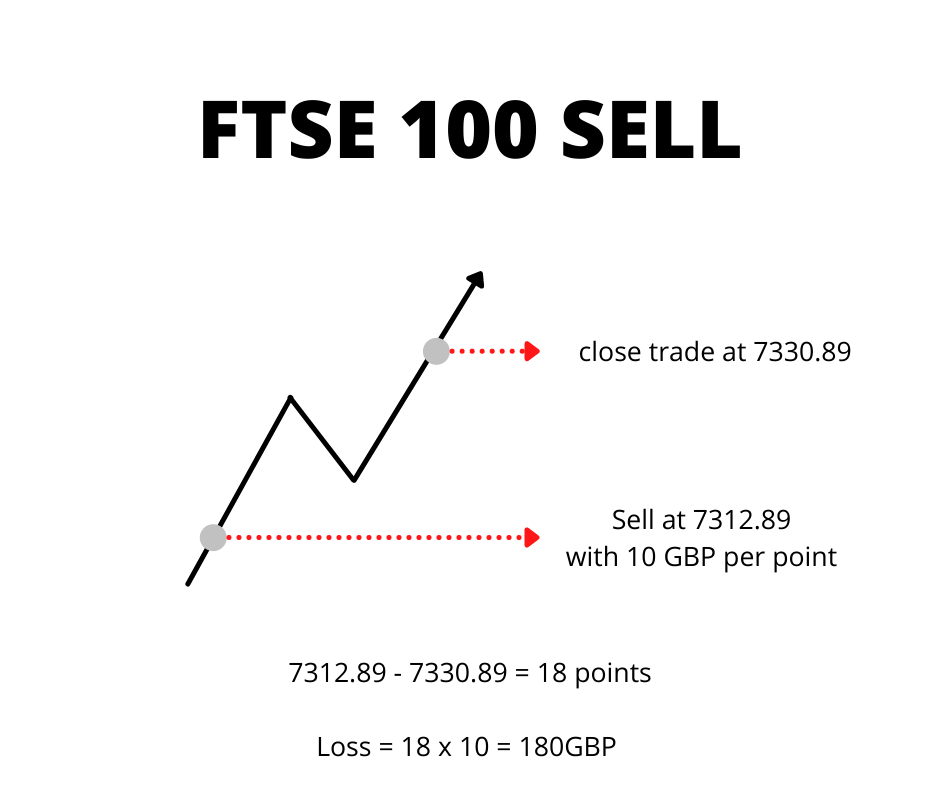
Financial Spread Betting FTSE 100 example:
When you do financial spread betting on indices, you do so in terms of GBP per point. A point in trading is the last digit before the decimal. In the case of the FTSE100, if you were trading at a price of 7312.89, the ‘2’ is the point. So following this, if you were to sell short the FTSE100 at 7312.89 with a size of 10, betting that its price would go down, but unfortunately in a few days the price went up to 7330.89 – you would lose 18*10 = 180 GBP (excluding overnight costs). The price went 18 points against you.
As you can see the basics of financial spread betting aren’t that complicated, because it works in terms of GBP per pip/point.
Interested in FX spread betting? Check our article here.
Ready to start trading? Check some of the top spread betting brokers.
You can also use our spread betting broker comparison tool.
Key Features of Spread Betting
Leveraged Trading
Spread betting is typically leveraged, meaning:
- You only put down a deposit (margin) to take a larger position
- Leverage magnifies gains and losses
For example:
£1,000 with 1:30 leverage can control a position worth £30,000.
While leverage increases potential returns, it also increases risk — and losses can exceed your initial deposit if not managed properly.
No Ownership of the Underlying Asset
Spread betting doesn’t involve owning the actual security (like shares). Instead, you’re betting on the price movement of that security.
Profits & Losses Calculated Per Point Movement
Your profit/loss is calculated as:
(Price exit – Price entry) × your stake per point
This applies both when markets rise and fall.
Financial Spread Betting vs CFDs
Both spread betting and CFDs (Contracts for Difference) allow leveraged speculation, but there are important differences:
| Feature | Spread Betting | CFDs |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Ownership | No | No |
| Leverage | Yes | Yes |
| Profit/Loss Basis | Per point movement | Per point movement |
| Tax Treatment (UK) | Generally tax-free (no CGT)* | Pay Capital Gains Tax |
| Cost Structure | Spread + Financing | Spread/commission + Financing |
| Suitable For | UK & Ireland traders primarily | Global traders worldwide |
*Tax treatment varies by country and your personal circumstances — always consult a tax advisor.
Regulation of Spread Betting
Financial spread betting is a regulated activity in the UK and Ireland, overseen by authorities like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Regulation means brokers offering spread betting must:
- Hold appropriate licenses
- Segregate client funds
- Provide risk warnings
- Adhere to capital adequacy and compliance rules
In jurisdictions outside the UK & Ireland, spread betting might not be available or may carry a different regulatory treatment.
Where Spread Betting Is Available
Spread betting is most common in:
- United Kingdom
- Republic of Ireland
In many other countries, similar products exist under different names (like CFDs) due to local regulatory frameworks.
Where Spread Betting Is Available
Spread betting is most common in:
- United Kingdom
- Republic of Ireland
In many other countries, similar products exist under different names (like CFDs) due to local regulatory frameworks.
Spread Betting Platforms & Tools
Most brokers offering spread betting also provide powerful platforms:
MetaTrader 4 & MetaTrader 5
- Popular, reliable platforms
- Advanced charting & indicators
- Algorithmic trading support
Proprietary Web & Mobile Platforms
Brokers also offer web and mobile trading apps with:
- Real-time pricing and alerts
- Watchlists and order placement tools
- Integrated news and analysis
Risk Management in Spread Betting
Spread betting is high risk — especially when leveraged.
Stop Loss & Take Profit Orders
These order types help lock in gains and limit losses.
Position Sizing
Trade size should match your risk tolerance — never risk too much on a single position.
Negative Balance Protection
In some regions (e.g., UK with FCA regulation), retail traders benefit from negative balance protection, preventing loss beyond your account equity.
Spread Betting Strategies
Trend Following
Ride long-term price trends using moving averages.
Range Trading
Trade support and resistance within bounded price ranges.
News & Event Trading
React to economic data releases and central bank announcements.
Hedging
Use spread bets to hedge other positions (e.g., stock portfolios).
Spread Betting Strategies
Trend Following
Ride long-term price trends using moving averages.
Range Trading
Trade support and resistance within bounded price ranges.
News & Event Trading
React to economic data releases and central bank announcements.
Hedging
Use spread bets to hedge other positions (e.g., stock portfolios).
Drawbacks & Risks
While spread betting offers flexibility and tax advantages, there are downsides:
Highly Leveraged
Leverage makes losses bigger — especially with high volatility.
Market Gaps
Markets often gap on news, potentially hitting stops at worse prices.
Costs Add Up
Overnight fees and wide spreads in volatile markets can erode returns.
Limited Availability
Not all regions offer spread betting (e.g., not available in US/Canada).
| Feature | Spread Betting | CFDs | Stocks | Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leverage | Yes | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Tax Benefits (UK/IE) | Often tax-free | Taxed | Taxed | Taxed |
| Cost Type | Spread + Financing | Spread/Commission + Financing | Commissions + Spread | Premiums + Fees |
| Suitable for Directional Trading | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Overnight Charges | Yes | Yes | No | Varies |
| Market Access | Forex, Indices, Commodities | Broad | Equities Only | Derivatives |
How to Get Started with Spread Betting
- Choose a regulated broker that offers spread betting (UK/Ireland for tax treatment).
- Open a spread betting account (verify identity).
- Fund your account (bank transfer, card, e-wallet).
- Explore demo account before real money.
- Analyse markets and choose your strategy.
- Place your first bet with appropriate risk controls.
- Monitor and exit using stops or profit targets.
FAQs
What is financial spread betting?
Financial spread betting is a tax-efficient (in some regions) way to trade markets without owning assets — you bet on price direction using leverage.
Is spread betting risky?
Yes. Leveraged positions can lead to significant losses and may exceed your initial margin if not managed carefully.
Can I lose more than my initial bet?
With negative balance protection (where offered), retail traders cannot lose more than their account balance.
Do I pay tax on profits?
In the UK and Ireland, spread betting profits are often tax-free, but you should consult a tax professional for your situation.
What markets can I trade with spread betting?
Forex, indices, commodities, shares indexes, and cryptocurrency markets are commonly available, depending on your broker.