Forex (FX) trading works in a similar manner to trading traditional financial markets such as stocks, indices, commodities, except that when you trade FX, you wager on the rate of exchange between two currencies. For example, if you bet on EUR/USD going up (buy), you’re betting on the euro’’s value versus the US dollar increasing. As a result, if the EUR/USD rate rises, you will profit; if it falls, you will lose. When you short sell EUR/USD, you’re wagering that the Euro will lose value against the US dollar. Normally when you trade Forex you do so in terms of lots. It’s also normal practice that the contract size for 1 lot in Forex is equal to 100,000. We will explain in more detail with examples in the following paragraphs exactly how fx trading works.
FX and CFD trading allows you to utilize leverage when placing trades because it is a derivative product (you don’t own the underlying asset; you simply bet on its price). Leverage is the ability to borrow money from forex and cfd brokers in order to put larger bets with less cash. When compared to trading without leverage, this helps you to optimize profits on your money because the amount necessary to open trades is reduced. However, while potential returns may be greater when trading with leverage, trading with leverage also raises the dangers involved with trading and can result in larger losses.
MT4 is one of the most popular trading platforms among retail investors. You can check forex and cfd brokers which offer MT4 here.
You can check the differences and similarities between spread betting and cfd trading here.
FX Trading examples:
As previously mentioned, FX trading works in terms of lots. This means that if I were to use a trade size of 1 lot (contract size 100,000), I would earn or lose roughly 10 USD for every pip move in the price. Keep in mind that the amount per pip for size of 1 lot may differ depending on the pair which you trade. A pip is normally the 4th decimal of the quoted FX pair. The exception for this rule are JPY pairs where the pip is the 2nd decimal.
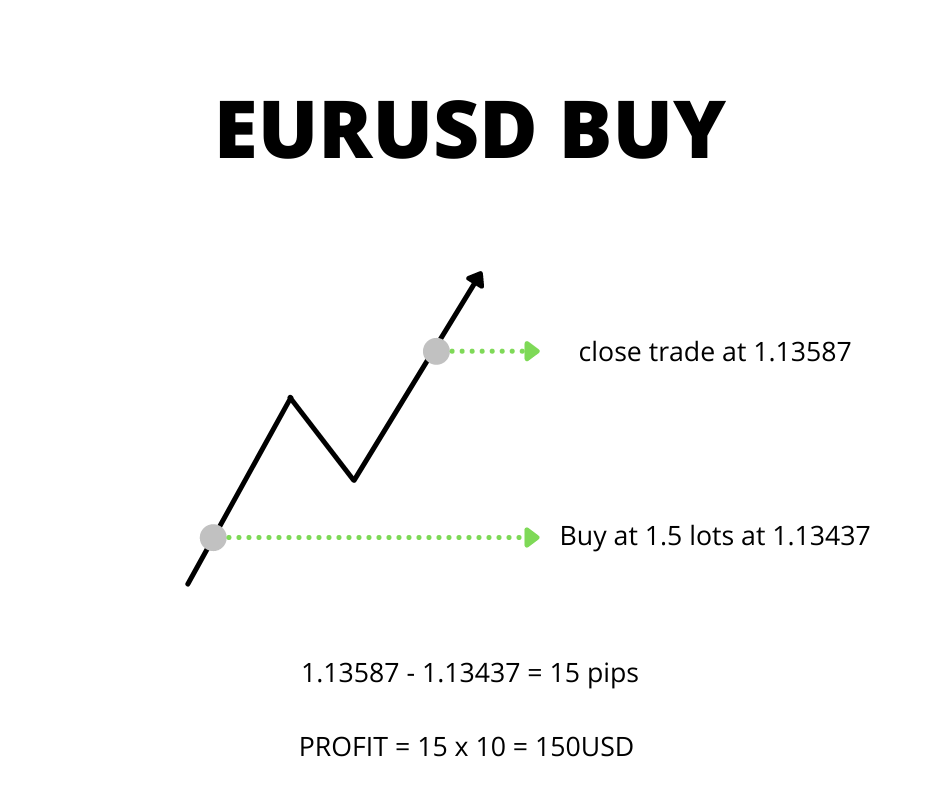
If I were to buy EURUSD at 1.13437 with trade size of 1 lot, thus betting that the euro will appreciate against the dollar, and in a few days the EURUSD rate went up to 1.13587, this means that the price moved up by 15pips, your profit would be 150USD (overnight fees aren’t taken into account).
If you were to sell USDJPY with a trade size of 1.5, at 113.550 and a few days later the USDJPY rate fell to 113.350, the price would have moved by 20 pips thus giving you a profit of roughly 265USD after conversions (overnight fees not included).
Ready to start FX trading? Find your Forex broker here.
You can compare cfd brokers here.
If you want to know more about how to trade CFDs on a specific market check our guides on: indices and shares.
Try finding your broker using our unique filtration system.